Can Ozempic Help with PCOS? What The Research Says
If you have PCOS, you may know how frustrating weight loss can be. You might follow strict diets, exercise regularly, and still struggle to see results. The constant cravings, hormonal ups and downs, and pressure to “manage stress” all while battling the challenges of trying to lose weight - can make it feel like an endless cycle.
It’s understandable that many women with PCOS start exploring weight loss medications such as Ozempic. But that often brings its own worries - questions about safety, side effects, and whether the information available actually applies to women with PCOS.
In this blog, I’ll walk you through how the medication works, what the research says, the possible benefits and side effects, and whether it could be a helpful option for managing your symptoms.
What Is Ozempic?
Ozempic is a medication that helps people manage type 2 diabetes. It contains an ingredient called semaglutide, which belongs to a group of medicines known as GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) receptor agonists.
You’ve probably also heard of Rybelsus, Wegovy, and Mounjaro - they’re often mentioned alongside Ozempic because they work in a similar way. Wegovy, Rybelsus, and Ozempic all contain the same ingredient, semaglutide, but they’re used for slightly different purposes or in different ways.
Ozempic - A weekly injection used to manage type 2 diabetes.
Rybelsus - A daily tablet used for type 2 diabetes.
Wegovy - A higher-dose injection approved for weight loss.
Mounjaro - A dual-hormone injection (GLP-1 and GIP) approved for weight loss.
All these medications work similarly, even though they have different brand names, forms and doses. They all belong to the same family of medicines called GLP-1 medications.
What Are GLP-1 Medications?
GLP-1 medications, such as Ozempic, mimic a natural hormone in the body called GLP-1. These medicines were first developed to help people with type 2 diabetes manage blood sugar levels more effectively, but it was noticed that the medications also caused weight loss.
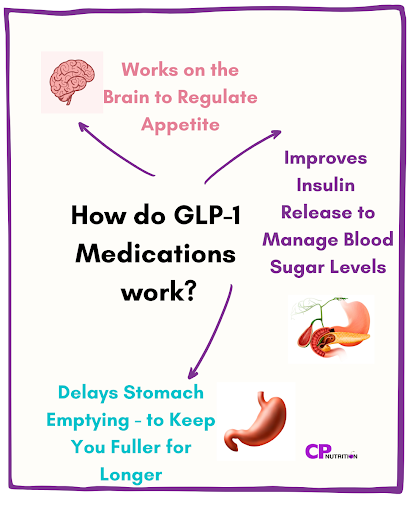
How Do GLP-1 Medications Work?
GLP-1 medications work alongside your body’s own hormones to help balance blood sugar and appetite by:
Improving insulin response: GLP-1 medications help the body release insulin more efficiently after meals, when blood sugar levels rise. It also lowers another hormone called glucagon, which normally raises blood sugar. Together, these actions help the body use insulin more effectively and maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Slowing digestion: These medications also slow down how quickly food leaves the stomach. This slower digestion helps you feel fuller for longer.
Regulating appetite: They also help the brain recognise when you’re full, which naturally reduces appetite.
How Ozempic May Help Women with PCOS
Ozempic may help women with PCOS in several ways. Research suggests it could play a role in improving insulin sensitivity, supporting weight management, and even helping to restore menstrual regularity and fertility. Let’s take a closer look at what the evidence says so far.
1.Improving Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance affects around 35–80% of women with PCOS (1). It means that while the body still produces insulin, the cells don’t respond to it properly. This causes insulin levels to stay high, which can signal the ovaries to produce more hormones, such as testosterone. These excess “male-type” hormones can lead to symptoms like acne, excess facial or body hair, thinning hair and irregular periods.
Ozempic may help improve insulin resistance by improving insulin sensitivity and supporting weight loss. For women who are in a bigger body, weight loss may lead to improvements in how the body uses insulin and subsequently improvements in PCOS symptoms (2.)
2. Supporting Weight Loss
A recent review of four clinical trials involving 176 women with PCOS found that treatment with semaglutide and liraglutide (another type of GLP-1 medication) injections significantly reduced body weight, waist circumference, and testosterone levels (3).
Another study focused on women with PCOS who struggled to lose weight through diet and exercise alone; 27 women were treated with weekly semaglutide injections for three months and, on average, lost 7.6 kg (4) .These results are promising for women who find it difficult to achieve weight loss through lifestyle changes alone.
There’s also growing interest in PCOS weight loss pills, such as Rybelsus for PCOS, which contains the same ingredient as Ozempic (semaglutide) but in tablet form.
In a clinical trial, people taking Rybelsus over 26 weeks lost more than 5% of their body weight and improved their blood sugar levels (5). Since many people with PCOS struggle with insulin resistance and weight gain, Rybelsus may offer similar benefits. It’s approved for type 2 diabetes but is sometimes prescribed off-label for PCOS. More research is still needed to understand its full potential and limitations.
3. Regulating Menstrual Cycles
Irregular or missing periods are common in PCOS and are often linked to insulin resistance and hormonal imbalance. High insulin levels can disrupt the ovaries usual production of hormones, which impacts ovulation and leads to irregular periods. Improving insulin sensitivity and reducing excess weight can help lower insulin levels, balance hormones, and support more regular cycles.
In one study, women with PCOS who hadn’t seen results from diet and exercise alone started weekly semaglutide injections. After six months, around 80% got their periods back and lost at least 5% of their body weight, along with better blood sugar control (4). These results look encouraging, though more research is needed to confirm the long-term benefits.
This improvement in cycle regularity has also led many women to wonder if GLP-1 medications like Ozempic can help restore periods, could they also support fertility?
4. Enhancing Fertility
A review of 11 clinical trials involving 469 women with PCOS found that those who took GLP-1 medications had higher natural pregnancy rates and more regular periods compared to those who didn’t (6). Researchers believe this may be because these medications can improve insulin sensitivity, balance hormones, and support weight loss - all of which can help the body ovulate more regularly.
That said, GLP-1 medications aren’t recommended during pregnancy. Manufacturers advise stopping semaglutide (Ozempic or Wegovy) at least eight weeks before trying to conceive (7).
Fertility can be influenced by many factors, but for women who struggle with PCOS, the early research looks encouraging - even though more evidence is still needed. If you’re planning to start a family, it’s always best to speak with your doctor before starting or stopping any medication.
Ozempic Dosage and Use
Ozempic is taken once a week as a small injection under the skin - usually in your tummy, thigh, or upper arm. It’s best to take it on the same day each week to keep things consistent.
Most people start with 0.25 mg once a week for the first four weeks, which helps the body adjust to the medication. From week five, the dose is usually increased to 0.5 mg weekly (8).
Ozempic should always be used under medical supervision, and your doctor will guide you with dosing and duration.
Side Effects and Risks
Like most medications, Ozempic can cause side effects which can include:
Nausea
Bloating
Tiredness or fatigue
Headaches
Heartburn
Mild stomach discomfort
More serious side effects are rare but can include pancreatitis or gallbladder issues. Additionally, Ozempic has a boxed warning that it may increase the risk of thyroid cancer.
Ozempic is not advised during pregnancy or breastfeeding. If you have a history of pancreatitis or thyroid tumours, your medical provider will guide you on the safest options. Always speak with your doctor before starting or continuing treatment.
Medication Interactions
Ozempic can interact with certain other medications including diabetes medications such as insulin and sulfonylureas and certain antibiotics.
It’s important to have a medical review before combining any medications, so your doctor can make sure your treatment plan is safe and effective (9).
Is Ozempic Approved for PCOS?
You may be wondering now - is Ozempic approved for PCOS?
Ozempic isn’t currently approved for PCOS. It’s licensed to treat type 2 diabetes only. However, some doctors may prescribe it off - label for women with PCOS, particularly when insulin resistance or weight gain are major concerns. Ozempic may also be prescribed to help manage PCOS symptoms.
To understand your options, it’s best to speak with your healthcare team, who can guide you on whether this medication could be suitable for you.
Whether you decide to use a GLP-1 medication or not, it is still helpful to focus on ways to optimise your diet and lifestyle behaviours to manage your PCOS. Although these medications can lead to a reduction in how much you eat, it is still important to consume a good quality diet including lots of wholegrains, plant based proteins, oily fish, lean meats, a variety of fruits and vegetables, nuts and seeds and healthy fats from things like olive oil, and avocados, and using plenty of herbs and spices. A dietitian can support you with optimising your diet for PCOS whilst taking ozempic or other glp-1 medications.
Conclusion
Ozempic may offer new hope for managing some PCOS symptoms, but it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution. The research so far looks encouraging, though more studies are still needed to fully understand its long-term safety and benefits.
If you’re thinking about trying Ozempic or a similar GLP-1 medication, chat with your doctor or endocrinologist first. They’ll help you figure out what’s right for you and your goals.
And remember - medication is just one piece of the puzzle. Long-term PCOS care also means nourishing your body with good food, moving in ways you enjoy, and caring for your emotional well-being.
You can read more about PCOS in our blog posts or subscribe to the free newsletter for evidence-based tips on women’s health and hormones.